The software landscape is rapidly evolving towards adaptive, self-writing programs that personalize user experiences rather than offering generic solutions. Sam Altman highlights this shift, envisioning tools that dynamically code and evolve according to individual needs.
Moltbot (formerly Clawdbot): A Milestone in AI Agents
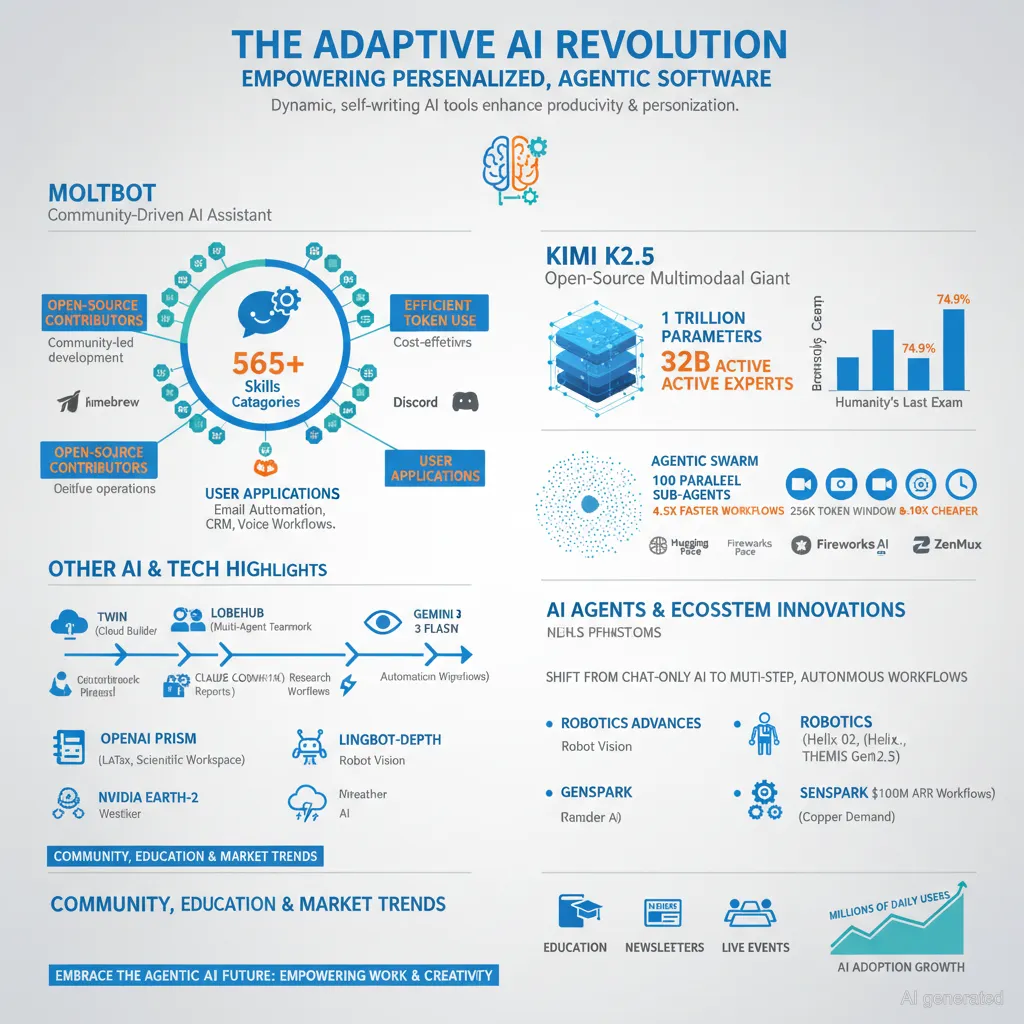
Moltbot, an AI assistant formerly known as Clawdbot, is gaining widespread attention in the AI community. After being asked by Anthropic to rebrand for trademark reasons, the platform emerged with a renewed identity and even stronger capabilities. It operates locally or on cloud servers and supports a vast ecosystem of “Skills”-plugin-like modules that enable the assistant to perform specialized tasks across various domains, such as DevOps, CLI automation, marketing, sales, and productivity tools.
Noteworthy features include:
– Over 565 community-driven Skills covering 32 categories.
– Seamless integration with services like Apple Music, Homebrew, and weather updates.
– Supports independent operation through Telegram, Discord, and AWS instances.
– Open-source development with thousands of contributors and continuous enhancements.
– Efficient token consumption methods that reduce usage dramatically.
Users report practical applications such as automated email management, research assistance, CRM development, voice-controlled workflows, and comprehensive doc management, showcasing Moltbot as a versatile AI co-worker expanding personal and organizational productivity.
Kimi K2.5: Cutting-Edge Open-Source Multimodal AI
Moonshot AI has unveiled Kimi K2.5, a fully open-source large language model that integrates text, image, and video inputs, positioning itself as a strong competitor to commercial heavyweights like GPT-5.2, Claude Opus 4.5, and Gemini 3 Pro. Highlights include:
– Over 1 trillion parameters with 32 billion active mixture-of-experts.
– Native multimodal understanding and generation, including impressive video comprehension.
– State-of-the-art benchmarks: 50.2% on Humanity’s Last Exam and 74.9% on BrowseComp.
– Agentic “swarm” feature enabling up to 100 parallel sub-agents executing complex workflows 4.5x faster.
– Extended 256k token context window, supporting long documents and multi-step reasoning.
– Competitive pricing around 8-10x cheaper than counterparts, making high-quality AI accessible.
– Available via APIs, Hugging Face, and platforms like Fireworks AI and ZenMux.
Practitioners praise Kimi for generating aesthetically rich websites, handling coding jobs, and performing visual tasks with notable success. Its open weights model facilitates on-premise use, fine-tuning, and customization without reliance on proprietary APIs, marking an important milestone in reducing AI centralization.
AI Agents and Ecosystem Innovations
Several platforms and innovations underscore the transition from chat-only AI towards complex agentic architectures:
– Twin: Cloud-native AI company builder with zero setup and robust scalability, focusing on reliable agent workflows. It avoids traditional API integrations by automating web interactions directly, aiming to solve production reliability issues with agents.
– LobeHub and Claude Cowork: Advanced agent orchestration platforms supporting multi-agent teamwork, stateful workflows, and human-in-the-loop approaches to handle variable tasks efficiently.
– Superagent by Airtable: Deploys multiple specialized AI agents in parallel for complex business research tasks, producing interactive, detailed reports called SuperReports rather than simple text dumps.
– Google’s Gemini 3 Flash includes Agentic Vision, combining code execution with image understanding to enhance visual AI capabilities such as zooming, annotating, and performing computations on images.
– Open-source tools such as lobster-workflows offer deterministic AI pipeline orchestration, enabling reliable, repeatable agent workflows with approval gates.
This agentic shift enables AIs to perform multi-step, multi-domain workflows autonomously or semi-autonomously, improving task success rates and making AI practical for more complex, sustained work beyond simple Q&A chats.
Other AI and Technology Highlights
– OpenAI Prism introduces a LaTeX-native scientific workspace integrated with GPT-5.2, facilitating collaborative writing with real-time citation management, equation understanding, and proofreading in a single interface.
– LingBot-Depth from Ant Group enhances embodied AI by refining noisy depth data from RGB-D cameras, significantly improving robots’ 3D world perception and manipulation.
– NVIDIA announced Earth-2, an open-source AI weather forecasting system with models capable of 15-day forecasts and rapid storm prediction.
– Robotics advances showcase enhanced humanoid models like Figure’s Helix 02 and Westwood Robotics’ THEMIS Gen2.5, which perform complex tasks with real-time manipulation while walking.
– AI platforms like Genspark achieve $100 million ARR with autonomous workflows including AI voice dictation and custom workflow automation.
– Market insights show surging copper demand driven by AI tech expansion.
– AI-powered automations, voice cloning, presentation generation, and marketing growth hacks continue expanding in usability and sophistication.
Community and Educational Efforts
– Educational resources include foundational AI and LLM courses from Karpathy, OpenAI Cookbook, Hugging Face, and DeepLearning.AI.
– AI-related newsletters, tutorials, and live events are fostering collaboration and deeper understanding.
– Studies on better prompting techniques and AI creativity enhancements help broaden model capabilities.
– Discussions emphasize the necessity of generalist skill sets, deliberate practice with AI tools, and embracing the agentic future rather than fearing automation.
Market and Industry Trends
– AI adoption is drastically increasing worldwide with millions of daily users integrating AI in their workflows.
– The AI ecosystem is diversifying into specialized niches that generate sustainable revenue beyond saturated markets.
– Investments and strategies are pivoting towards reliability and workflow-oriented tools rather than mere user counts.
– Open-source models gaining parity with proprietary labs is shifting the competitive landscape.
Summary
The current AI revolution is marked by a shift towards adaptive, agentic software that works collaboratively with humans to automate complex tasks. Tools like Moltbot signal a new era where AI assistants are customizable, community-driven, and deeply integrated into daily routines and business operations. Concurrently, open-source models such as Kimi K2.5 are narrowing the gap with closed commercial models, offering accessible, scalable AI multimodal understanding and generation capabilities. This empowers a broader base of developers and operators to harness AI’s potential.
Additionally, innovations in AI agents, robotics, and scientific tooling demonstrate practical advances, while educational resources and community engagement foster skill development appropriate for this transformative era. Companies and individuals adapting to this paradigm are positioned to partake in the vast opportunities AI offers, as the technology continues to evolve rapidly toward shaping the future of work, creativity, and industry.