The landscape of AI coding agents and related technologies has witnessed remarkable advancements and fascinating developments across multiple domains. Experts and innovators like Andrej Karpathy, Shawn Wang, Alex Albert, McKay Wrigley, and Benjamin Akar have contributed rich content on aspects such as vibe coding workflows, agent architectures, live app building streams, and agent automations, pushing the frontier of AI-powered coding.
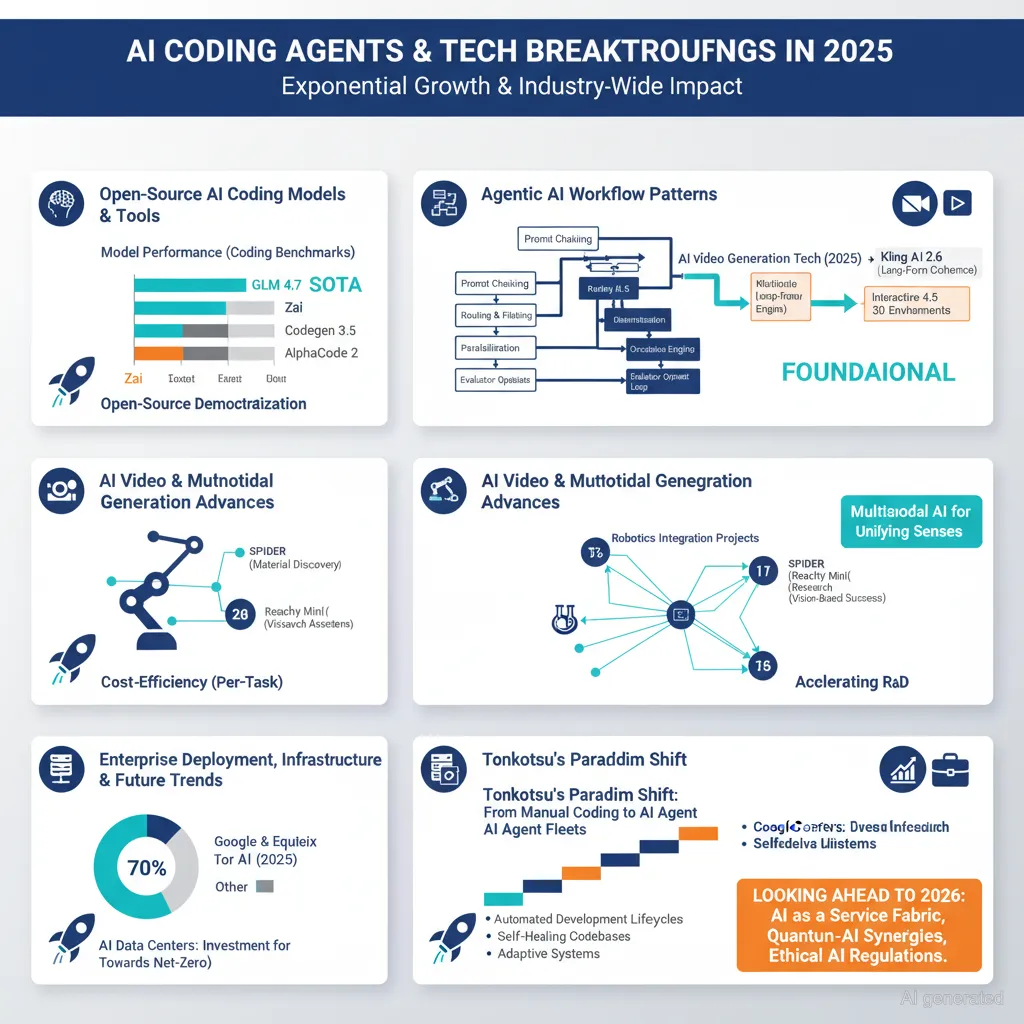
A major theme is the rise of open-source models and tools, with impressive new releases like Zai’s open-source model outperforming established competitors while offering significant cost reductions and superior UI quality. GLM 4.7, now accessible via platforms like Okara, has set new state-of-the-art benchmarks in coding, multi-step reasoning, and large context window usage, challenging closed-source models. MiniMax M2.1 has emerged as another strong open-source agent for coding tasks and vibe builds.
Claude remains prominent as a user-friendly AI assistant with built-in comprehensive web app features requiring no technical setup, making it ideal for non-technical users seeking powerful LLM experiences. Its capabilities have been showcased through quick developments like Chrome extensions that enable chat-based analysis of Twitter timelines for content insights.
Agentic AI workflows and patterns have been analyzed extensively, highlighting critical workflow architectures such as prompt chaining, routing, parallelization, orchestration, and evaluator-optimizer loops. These form the backbone of enterprise agentic systems, emphasizing the value of building from simple workflows before adopting complex agents. Emerging best practices also cover orchestration of subagents within skills for optimized context management.
Innovations extend into AI video generation and editing, with technologies like Higgsfield’s WAN 2.6 and Kling AI 2.6 transforming video creation by adding motion control, lip sync, and synchronized gestures with high fidelity. Nano Banana Pro’s image generation quality underpins compelling slide and advertising creative production. Similarly, Seedream 4.5 leads in realistic AI-generated human portraits, outperforming competing models in preserving identity and visual consistency.
Scientific and technical research has advanced foundational AI capabilities. For example, reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards (RLVR) has become critical in LLM post-training, enabling continual learning. Vision models have demonstrated that causal prediction alone suffices for strong visual understanding without complex reconstruction or contrastive loss. New methods in language modeling, such as LLaDA2.0’s diffusion-based approach, significantly speed up generation while maintaining quality.
The industry is witnessing growing integration of AI with robotics, exemplified by projects like Facebook’s open-source SPIDER framework for dexterous humanoid and hand retargeting and Reachy Mini’s agent-enabled robotic dexterity demonstrations. Tesla’s vision-first approach to autonomy has proven robust during power outages where LiDAR-dependent systems failed, underscoring the potential for scalable, vision-based autonomous systems.
In energy infrastructure, major corporations like Google are moving towards owning clean power supply chains to better match AI data center demand, acquiring platforms like Intersect for solar and battery co-location. Equinix explores modular nuclear reactors to secure AI workload baseload power in Europe, highlighting the emerging role of energy certainty in AI scaling.
AI video and motion capture breakthroughs have democratized Hollywood-level production with tools like Kling AI motion control and Seedance 1.5 audiovisual synchronization models. These tools enable detailed, realistic character animations and AI-generated cinematic content directly from simple inputs or templates.
Enterprise AI deployments are focusing on system reliability, monitoring, and evaluation, with pipelines built on vector databases like Qdrant, orchestration frameworks like LangGraph, and tracing tools ensuring production readiness of RAG workflows. New open-source projects like Airweave are pioneering intelligent, multi-source context retrieval crucial for complex agentic queries.
The AI ecosystem is also shaped by evolving business models and workforce transformation. New service firms specializing in implementing AI agents within traditional companies are expected to emerge, alongside startups leveraging AI agents from inception to disrupt traditional workflows and scale services more efficiently.
Multimodal AI is gaining importance as research labs acknowledge text-only data is insufficient for true AGI. Embodied learning leveraging continuous sensor data (video, robotics, physics experiments) offers vastly richer activation patterns, enabling models to overcome limitations of training only on static text. This shift is pivotal for advancing general intelligence.
In software development, the emergence of tools like Tonkotsu highlights a significant paradigm shift from manual coding to managing fleets of specialized AI agents that plan, execute, and supervise development tasks, greatly accelerating productivity.
Highlights from scientific research include advances in AI reasoning, such as the Generative Adversarial Reasoner that optimizes stepwise logic in math-solving LLMs, and innovations in system performance that accelerate research via AI-driven code generation and testing.
At the user level, practical AI tools for productivity and business growth, including Excel formula automation, video editing workflows, AI-assisted coding, and agentic personal assistants, exemplify how everyday tasks and creative processes are being transformed by accessible AI.
In summary, 2025 has been a breakthrough year marked by exponential growth in AI coding agents, multimodal learning, robotics integration, scalable infrastructure, and novel business models. The trajectory points to 2026 as the year where editing video content with AI, robust AI agent deployment in enterprises, and embodied AI research will catalyze further leaps toward artificial general intelligence and widespread industrial transformation.
