This review synthesizes recent diverse news and developments in AI, robotics, engineering, and technology sectors, highlighting breakthroughs in autonomous AI systems, large language models (LLMs), hardware innovations, and applied AI in various industries.
HP Anyware and Remote Work Enhancements
HP introduced HP Anyware, a remote management solution to enhance workstation accessibility, exemplified by a user integrating it with the HP Z6 G5 workstation equipped with powerful RTX PRO 6000 Blackwell Max-Q GPUs. This highlights ongoing efforts to improve remote workflows and compute accessibility for professional users, particularly in demanding environments like 3D graphics and design.
Advances in AI Models and Autonomous Agents
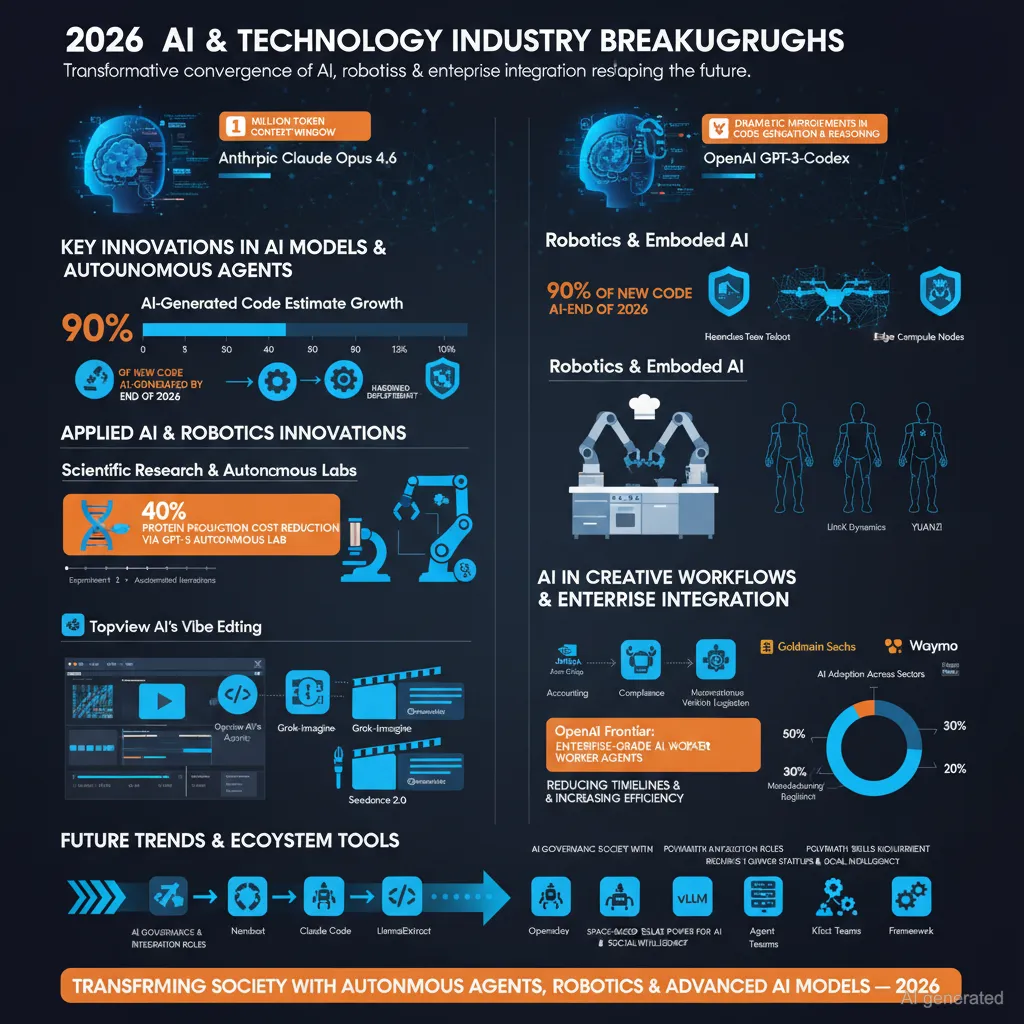
The AI community witnessed significant updates with the releases of Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.6 and OpenAI’s GPT-5.3-Codex, both showing dramatic improvements in code generation, reasoning, and planning capabilities. Opus 4.6 supports a one million token context window, enhanced agentic behavior, and mathematical reasoning, while Codex 5.3 boasts faster inference with better efficiency and mid-task steerability. These models enable a new era of autonomous software development where AI agents actively plan, execute, test, and refine codebases with minimal human intervention-ushering a paradigm shift to “agent era” productivity.
Notably, AI agents have evolved into collaborative teams, exemplified by frameworks like OpenClaw and Claude Code, which orchestrate multiple specialized agents working in parallel on complex tasks. Security concerns around AI agents prompted hardening guides and token usage dashboards to ensure safe deployment. The rise in AI-written production code is now mainstream, with estimates suggesting over 90% of new code could be AI-generated by the end of the year, fundamentally transforming software engineering workflows.
Benchmarks and evaluations have become more transparent and community-driven, with initiatives like Community Evals and leaderboards for model comparisons including GPQA, HLE, and MMLU-Pro. Open-source models such as Kimi K2.5 have gained traction for offering competitive performance at drastically reduced costs compared to proprietary alternatives.
Additionally, breakthroughs in model editing techniques, such as AlphaEdit, offer reliable methods to update language model knowledge continuously without degrading existing capabilities, promising better long-term maintenance of AI knowledge bases.
AI Applications in Scientific Research and Autonomous Labs
OpenAI’s collaboration with Ginkgo Bioworks demonstrated automated closed-loop scientific experimentation where GPT-5 autonomously designed, executed, and iterated over biological experiments, achieving a 40% reduction in protein production costs. Similarly, Google’s Gemini was integrated into advanced research workflows, including adversarial reviews of complex proofs and mathematical research with agentic feedback loops, enabling new scientific discovery methods.
In chemistry, a new autonomous system uses reinforcement learning to conduct precise molecular bond cleavage with minimal human intervention, showcasing AI’s expanding role in physical experimentation.
Robotics and Embodied AI Innovations
Robotics developments ranged from humanoid platforms like LimX Dynamics, which combines full-stack hardware-software-OS integration for reliable field operation, to Boston Dynamics’ impressive physical robot demonstrations surpassing earlier capabilities. Infiforce’s YUANZI robot focuses on personalized humanoid companions designed for home environments, embodying emotional intelligence and adaptable modular design.
In service and industrial robotics, NEXFORM’s dual-arm NW-1 robot demonstrates sophisticated manipulation in hospitality and kitchen tasks powered by NVIDIA Jetson Thor chips, underlining the growth of modular, edge-compute-enabled platforms.
Drone racing research introduced fully neural, end-to-end flying systems capable of real-time decision-making, shedding traditional sensors and filters for purely learned control policies.
AI in Media, Creative Workflows, and Education
AI-enhanced creative tools have made drastic improvements in video generation, motion design, and game development environments. Examples include Topview AI’s Vibe Editing for programmatic professional motion graphics, OpenClaw-powered AI agents managing video editors, and AI models generating entire game assets and multiplayer game logic without coding.
Google and xAI (Elon Musk’s AI company) have made impressive strides in image and video AI with models like Grok-Imagine-Image and Seedance 2.0, which rival or surpass industry standards in cinematic quality and multi-shot coherence.
Additionally, educational programs integrate AI tools for data engineering, AI research internships, and applied AI mentorships to cultivate new talent in emerging AI disciplines.
Industry Integration and Enterprise AI Adoption
Leading enterprises such as Goldman Sachs and Waymo are deploying AI for complex workflows-accounting automation, compliance, client onboarding, and autonomous vehicle simulation-demonstrating the maturation of AI systems in regulated and high-stakes environments.
OpenAI’s Frontier platform exemplifies enterprise-grade AI worker agents integrated across multiple data systems with governance and auditability, significantly reducing operational timelines and increasing efficiency.
NVIDIA, Siemens, and other industry leaders emphasize digital twin technologies, distributed AI serving frameworks like vLLM-Omni, and orbital data centers powered by space-based solar energy as foundational enablers of scalable AI infrastructure.
Future Trends and Economic Impact
Experts predict a substantial transition where traditional human jobs will be increasingly augmented or replaced by AI, with new roles emerging around AI governance, monitoring, and integration. Marketing, social intelligence in AI, and AI-driven small team startups are identified as high-growth areas.
There is widespread consensus that succeeding in this emerging era requires polymath skills-including technical, design, and social capabilities-and mastery over AI tools to stay competitive.
Energy constraints for AI scalability are expected to be alleviated by space-based power solutions (SpaceX initiatives) and more efficient hardware, supporting continuous AI progress.
Notable Tools and Ecosystem Developments
– OpenClaw and Nanobot: Agent orchestration frameworks with varying complexity and scale.
– Claude Code and Codex CLI: Powerful AI coding environments and agent supervisors.
– LlamaExtract: Enhanced document processing with citation transparency.
– vLLM and mlx-lm: Open-source frameworks for serving multiple model modalities.
– Agent Teams and Swarms: Collaborative multi-agent systems for extended task execution.
– KISS Multi-Agent Framework: Simplified Python tools for multi-agent workflows with genetic prompt optimization.
Concluding Remarks
The convergence of advanced AI models, autonomous agents, robotics, and integrative enterprise systems marks a transformative period in technology and society. The emphasized shift from tool usage to autonomous agent ecosystems heralds unprecedented productivity, innovation acceleration, and reshaped labor dynamics. The rapid pace and breadth of progress underscore the necessity for continuous learning, adaptability, and ethical considerations as AI permeates all facets of work and life.
