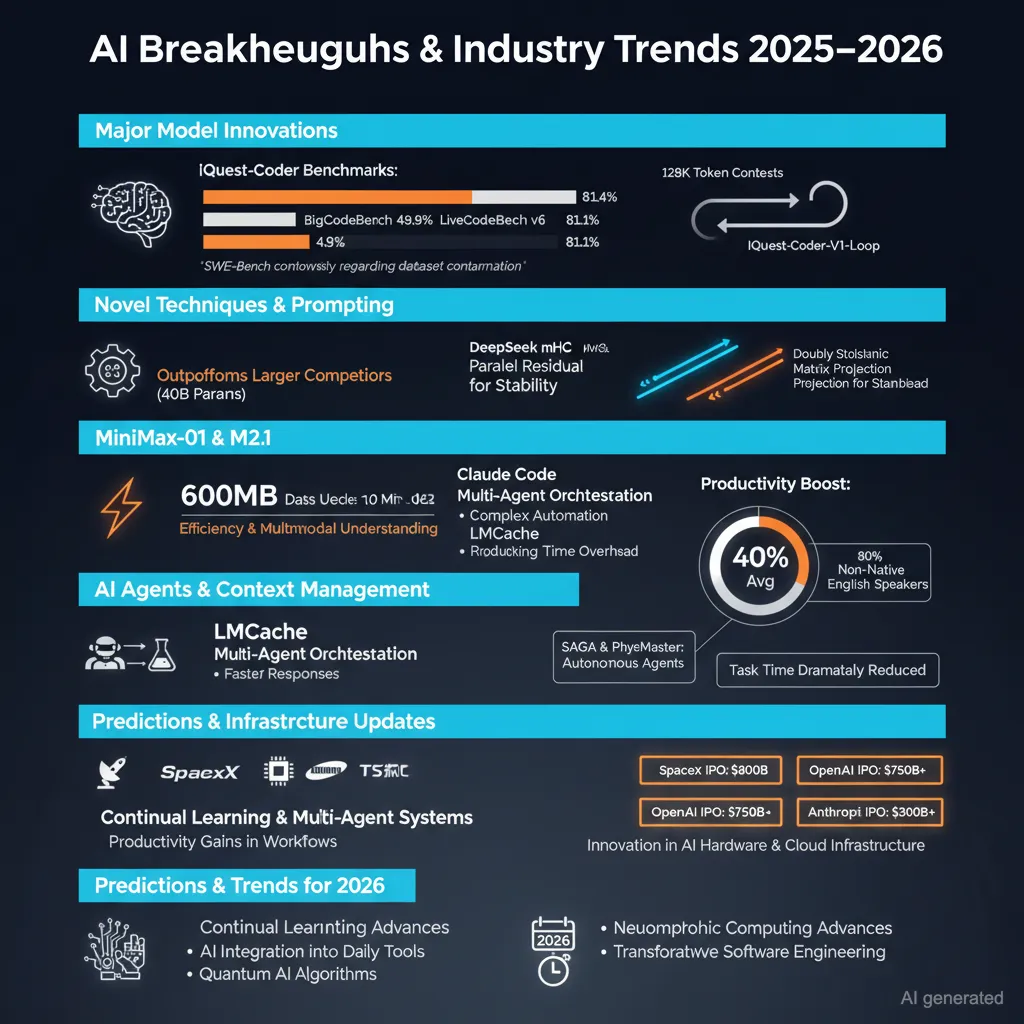
China’s IQuest-Coder Model Surpasses Larger Competitors
A new open-source code generation model called IQuest-Coder from Quest Research in China has demonstrated remarkable performance despite having only 40 billion parameters. The model outperforms Claude Sonnet 4.5 and GPT 5.1 on several benchmarks, including SWE-Bench (81.4%), BigCodeBench (49.9%), and LiveCodeBench v6 (81.1%). Supported by UBIQUANT, a major Chinese quantitative hedge fund with assets under management between CNY 70-80 billion (~$10-11 billion) and an average 24% return in 2025, Quest Research has pioneered bificated post-training producing two specialized model variants: “Thinking” models optimized via reasoning-driven reinforcement learning for complex problem-solving, and “Instruct” models tuned for general coding assistance. The IQuest-Coder-V1-Loop variant introduces a recurrent architecture optimizing the balance between capacity and deployment cost and natively supports very long contexts of up to 128K tokens. The model is hosted on Hugging Face and is expected to gain more inference provider support soon. However, it was later noted that its SWE-Bench benchmark might be compromised due to modeling artifacts involving inclusion of git history, advising caution in interpreting scores.
DeepSeek’s Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections (mHC) Architecture Advances Transformer Stability and Capacity
DeepSeek has unveiled mHC, an innovative transformer architecture modification that extends the residual connection from a single “highway” to multiple parallel pathways, allowing greater model capacity and improved topological complexity. Unlike previous “hyper-connection” designs, mHC imposes a strict mathematical constraint by projecting learned residual mixing matrices onto the Birkhoff polytope, enforcing doubly stochastic (row- and column-sum normalized) matrices. This restriction preserves the identity mapping essential to stable training by preventing exploding or vanishing signals during forward and backward passes, even in models up to 27 billion parameters. This architectural design achieves stable gradient flow, improved training loss (~0.02 decrease), and consistent gains on reasoning and comprehension benchmarks (BigBench Hard, DROP, GSM8K, among others), with only ~6.7% training time overhead. mHC represents a critical shift from unstructured residual expansion toward geometry-conscious connectivity, enabling scalable large models with enhanced performance and stability. The design leverages variants of the Sinkhorn-Knopp algorithm and extensive kernel fusion optimizations.
MiniMax-01 and M2.1: Breakthroughs in Efficient Transformers and Text/Multimodal Understanding
Built on the premise that 2025 is a breakthrough year for agent systems, MiniMax-01 introduced “Lightning Attention,” pioneering efficient scaling of linear attention mechanisms as alternates to classical Transformer architectures. These innovations include optimized mixture-of-experts communication, enhanced long-sequence handling, and efficient kernel implementations, delivering industry-leading performance on text and multimodal understanding benchmarks at low cost. The lessons and architecture from MiniMax-01 directly shaped the M-series, notably the M2.1 variant, which processes large datasets rapidly (e.g., 600MB of data in under 10 minutes). MiniMax earned recognition as a top upvoted paper on Hugging Face in 2025.
Stanford’s Verbalized Sampling: Novel Prompting Technique to Boost LLM Creativity and Diversity Without Retraining
Stanford researchers developed verbalized sampling (VS), a training-free prompting strategy that addresses the creativity loss in large language models (LLMs) caused by post-training alignment techniques like Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). RLHF, while improving safety, typically leads to mode collapse by favoring “safe” and predictable outputs, reflecting typicality bias in human preferences. VS bypasses this by prompting the model to generate a distribution of multiple responses along with their probabilities instead of a single answer, effectively recovering the model’s diverse pre-trained latent space. It improves creativity metrics by 1.6-2x and human-rated diversity by 25.7%, surpassing fine-tuned models without additional training. Variants like VS-based Chain-of-Thought reasoning further enhance diversity. This method leverages the model’s dual “personalities”: the original pre-trained generate-rich mode and the safety-constrained aligned mode.
OpenAI’s New Audio Model and Device Plans for 2026
OpenAI is preparing a new audio AI model slated for Q1 2026, designed to power an upcoming audio-first personal device combining natural and emotive speech synthesis with low latency and real-time interruption handling for full-duplex conversational interactions. This represents a merger of multiple teams focused on improving audio model speed, accuracy, and response. Technical leadership includes Kundan Kumar, a voice AI expert hired from Character.AI, alongside infrastructure rebuilds led by Ben Newhouse. The new voice model architecture aims to achieve unprecedented naturalness and responsiveness, suggesting a major leap forward for conversational AI on dedicated hardware.
Advances in AI Agents, Coding, and Context Management
Claude Code, Anthropic’s agentic coding platform, continues to evolve, now supporting agent swarms, collaborative agents, search assistants, and multi-context priority management, enabling sophisticated programmatic automation. Developers report extraordinary productivity gains, with complex data analysis and simulation tasks that once took days now completed in minutes. The accompanying Claude Agent SDK empowers users to build intelligent agents with minimal code, democratizing AI automation. Meanwhile, LMCache offers a persistent, shareable KV cache layer, dramatically reducing redundant LLM compute during multi-turn dialogs, yielding throughput gains and latency reductions across multiple agents. The emerging paradigm emphasizes continual learning, self-managed context, and multi-agent coordination for scaling both long-horizon tasks and agent reasoning.
Significant Progress in AI-Assisted Scientific Discovery and Research Productivity
Using LLMs in scientific research has led to average productivity boosts of 40%, with even higher gains (up to 80%) for non-native English speakers, as evidenced by analyses of millions of papers published through mid-2024. AI-powered autonomous agents like SAGA are pushing the boundaries of automated scientific discovery by dynamically evolving optimization objectives during experimental design across domains such as antibiotic development, materials science, DNA sequence design, and chemical process engineering. PhysMaster, a large language model agent tailored for computational physics, combines code execution, reasoning, and memory retrieval to reduce task durations from months to hours or days. These developments signal a transformative acceleration in research processes augmented by AI.
Industry and Infrastructure Updates
SpaceX announced plans to lower approximately 4,400 Starlink satellites from 550 km to 480 km altitude to enable faster atmospheric deorbiting in case of failure, thereby reducing space debris risk amid a crowded Low Earth Orbit (LEO). Samsung is shipping samples of its next-generation HBM4 DRAM, targeting mass production in 2026 to dramatically boost bandwidth for AI training hardware. Baidu’s AI chip division Kunlun filed for a Hong Kong IPO, signaling intensified competition in China’s semiconductor sector. TSMC’s 2nm-class N2 chip production, leveraging advanced gate-all-around transistor designs, promises notable efficiency gains critical for AI hardware advancements. Notable IPOs anticipated in 2026 include SpaceX ($800B valuation), OpenAI (potentially $750B+ raise), and Anthropic (~$300B valuation).
Trends and Predictions for 2026
Experts forecast 2026 as the year of continual learning, where AI models dynamically adapt and self-improve with minimal human intervention, potentially resolving long-standing alignment and scaling challenges. Multi-agent orchestration systems, capable of coordinating specialized AI subagents on complex workflows, will proliferate, impacting enterprises with AI-driven logistics, manufacturing, and knowledge work automation. The integration of AI becomes deeply embedded into everyday tools – browsers, editors, design platforms – rather than as separate “AI” products, revolutionizing workflows by seamless context injection and multi-modal capabilities. Voice and conversational AI will be prominent signals in advertising and user experience personalization.
Local deployment of LLMs for cognitive security and resilience against manipulation is encouraged. Running models locally allows deeper understanding of AI limitations and behaviors, mitigating influence from opaque server-side alignment or incentive structures. AI literacy, much like traditional literacy, is rapidly becoming essential.
Finally, AI agents are expected to transform software engineering dramatically, eliminating junior and mid-level developer workflows by automating routine coding tasks. Coding agents now operate at the OS level carving a new abstraction beyond simple autocomplete, executing file operations, bug fixes, and complex feature integration autonomously. This maturation aligns with greater tooling sophistication and a focus on “whole product” approaches that deliver end-to-end solutions rather than fragmented features.
Additional Noteworthy Research and Technologies
– NFC robotic skin with neuromorphic spike-based signals enables reflexive responses to hazardous stimuli without CPU latency.
– Urban and agricultural robots gain enhanced sensory modalities and autonomy.
– AI models trained with geometric constraints maintain stable representations improving capacity and training efficiency.
– Open-source LLMs from Korea and Japan reach state-of-the-art levels including massive Mixture-of-Experts designs with scalable inference techniques.
– Novel prompting and agent control methods improve reasoning speed, reliability, and multi-turn coherence.
– Privacy-preserving federated learning grows as foundational training approach across major tech firms.
– New reasoning-enhanced recommendation systems leverage world knowledge in e-commerce platforms.
– Advances in multi-task robotics controllers enable complex dexterous bimanual manipulation.
– Cutting-edge language model interpretability tooling becomes accessible on personal hardware.
Given these updates, 2026 promises to be a pivotal year heralding advancements in AI architecture, reasoning, agent orchestration, privacy-preserving learning, and integration into human workflows and industries.
