The news aggregation highlights a whirlwind of advancements and insights in AI, coding agents, robotics, education, research, and industry trends as they approach 2026. These developments point toward a profound transformation in software engineering, artificial intelligence applications, and the future of work.
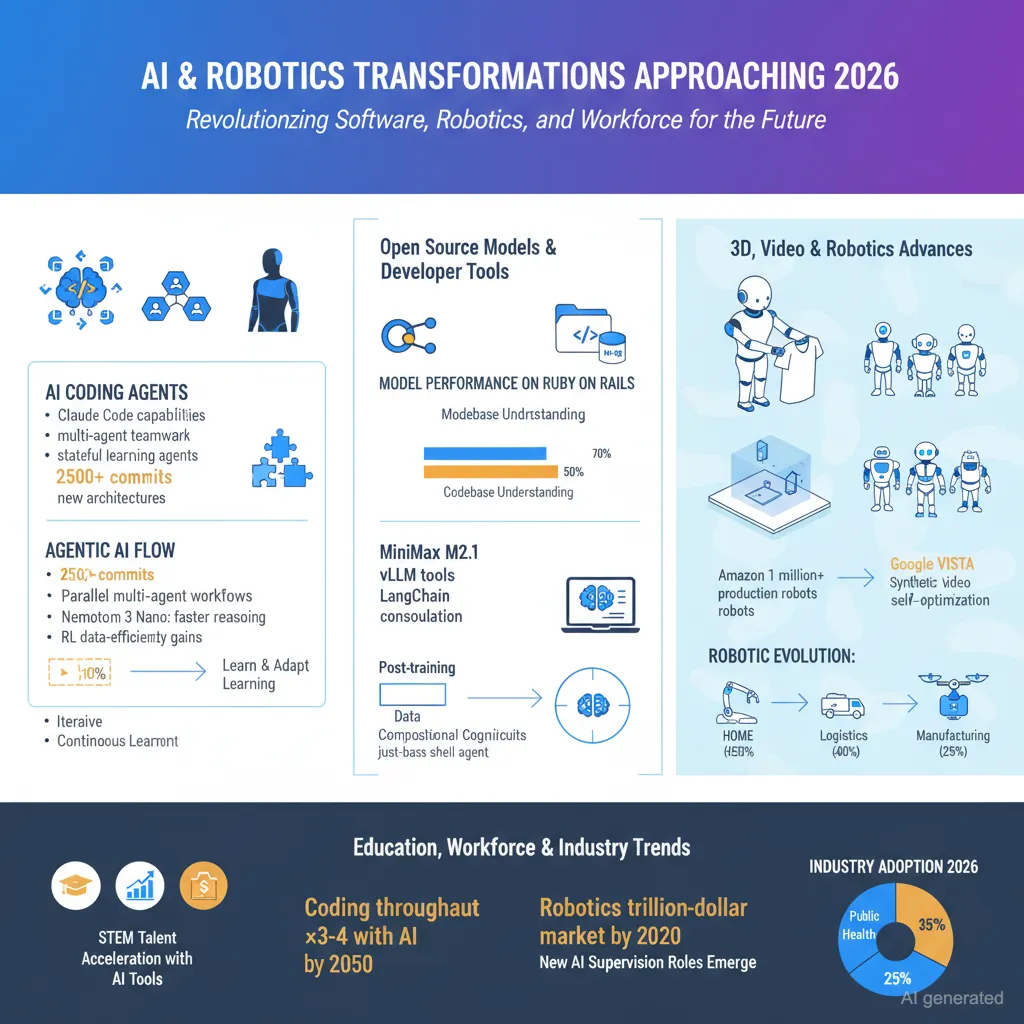
Claude Code and AI Coding Agents: Claude Code is emerging as one of the most powerful AI coding assistants, likened to Jarvis from Iron Man but still confined to virtual interactions without physical sensing capabilities. The upcoming release will allow users to build web and mobile apps with custom skills directly in the browser. With the integration of Claude Skills and specialized workflow orchestration, developers can spawn multiple agents working in parallel on complex projects, achieving unprecedented productivity gains. Stateful agents that learn and adapt with ongoing projects are further advancing the concept of sustained AI assistance. Performance improvements have been fueled by continuous updates (over 2,500 commits in a short span), and synergy with tools like Opus 4.5 has brought high proficiency in backend, database setup, and design tasks from simple prompts.
Aside from coding, Claude Code has demonstrated remarkable autonomous abilities, such as networking and integrating with proprietary systems like Lutron smart home infrastructure without prior knowledge, effectively replacing legacy applications. It’s also been containerized for Kubernetes, enabling 24/7 autonomous on-call engineering with hotfix and documentation generation capabilities. AI developers emphasize mastering fundamentals such as model architecture, inference, memory, and failure modes, which composes a solid foundation to build robust agents and products that last beyond fleeting hype cycles.
Agentic AI and New Architectures: The year 2025 saw breakthroughs in self-improving AI agents and multi-agent systems with coordinated teamwork, enabling agents to plan, execute, verify, and improve complex tasks across multiple domains. Papers revealed methods to optimize agent inference pipelines for speed and efficiency, cutting redundant computations and improving long-context management. System designs supporting long-lived agent identities with learning from past experience have shown significant improvements in reasoning efficiency and task success rates. New open reasoning models like Nemotron 3 Nano leverage mixture-of-experts architectures for faster generation with maintained accuracy.
Additionally, new sequence models challenging traditional transformers propose attention-free architectures based on Grassmann flows, achieving competitive results with linear scaling in sequence length. Reinforcement learning frameworks have improved data-efficiency dramatically for difficult tasks like content moderation by training with minimal labels but rich reasoning feedback.
Open Source Models and Community Tools: There has been notable momentum from Chinese and Western research labs pushing open-source models to new frontiers, with models like MiniMax M2.1 performing competently on complex codebases such as Ruby on Rails. Open ecosystems blending synthetic training data and post-training have enabled compositional reasoning circuits that foster cognitive core development. Community contributions include vLLM tools for easier inference management, playgrounds offering web UIs for interaction, and plugins enhancing memory and decision-making for agents.
Industry SDKs and libraries, such as LangChain’s consolidation for Google’s Gemini platform and innovations like just-bash (a TypeScript implementation of bash for agent shell interaction), further streamline AI coding workflows. Postgres coding has seen major quality leaps by integrating AI with version-aware documentation servers, instituting best practices, constraints, and index patterns that the AI leverages to generate superior schemas.
3D, Video, and Robotics Advances: AI-driven video editing and generation have matured rapidly. Breakthroughs include Google’s self-improving video generation agent VISTA, which autonomously rewrites prompts and judges outputs to enhance video quality with no retraining. Research on 4D scene understanding and dynamic object segmentation using transformers further improves spatial comprehension in computer vision tasks. Projects have demonstrated futuristic 3D projections on flat surfaces, eliminating conventional screens.
Home robotics are progressing in practical applications such as Isaac, a robot capable of folding laundry with camera and sensor precision, and Reachy Mini, an expressive open-source tabletop robot used for creative experiments like robot DJs synchronizing movement to AI-generated music. Industry production robots (e.g., Amazon’s fleet surpassing 1 million units) and specialized sector growth in agriculture and surgery signal a vast expansion in robotic presence across domains.
Education, Talent Development, and Workforce Evolution: Efforts in STEM education aimed at accelerated learning reveal that students with advanced math and coding proficiency achieve extraordinary research accomplishments at young ages, even contributing original discoveries to fields like astronomy. Online pipelines integrate high school through university-level training to scale talent development worldwide.
The career landscape for software engineers is undergoing a foundation shift; AI agents handle increasing portions of coding, testing, and deployment, moving humans into supervisory and strategic roles. Studies show tools like Cursor triple to quadruple code throughput initially, though quality tradeoffs require balancing. The new focus is on deciding what to build, testing rigorously, and setting well-defined specifications-skills that complement AI’s growing assistance.
Industry and Market Trends: According to Morgan Stanley and others, robotics is on track for explosive growth, with market values expanding into trillions by 2050. Public health systems, logistics automation, and manufacturing report significant adoption and productivity gains. The semiconductor and AI hardware ecosystem remains fiercely competitive, with major deals and innovations shaping future chips and inference technology.
In marketing and entrepreneurship, building vertical AI agents tailored to specific industries is identified as a major opportunity in 2026, allowing specialists to command premium prices over generic horizontal tools. Personal branding and systemic workflows amplified by AI yield financial independence for creators and developers.
Scientific Discoveries and Research Highlights: Several papers and findings spotlight transformational results-from confirming rare quantum spin liquid states to advances in medical and cognitive science that underline physical activity’s critical role in brain health and longevity. AI enables protein design at speeds and accuracy previously unfathomable, collapsing wet-lab timelines into prompt-based simulations with near-perfect real-world correspondence. Tools for explainable AI research, distributed memory, and symbolic execution are maturing, enhancing interpretability and system robustness.
General Technical and Workflow Insights: Best practices in logging, observability, and data engineering emphasize splitting hot and cold logs, automated filtering, and lifecycle management to balance cost and performance. Hands-on insights stress the importance of system thinking, building minuscule testable parts, and valuing fundamentals over flashy trends which often do not compound.
They also note the rising importance of AI orchestration layers (“wrappers”) that make sophisticated underlying tools accessible to non-technical users, indicating a future where interaction with AI agents happens through intuitive platforms rather than direct coding.
Summary: The panorama of these developments paints 2026 as a landmark year where AI, augmented coding, robotics, and human collaboration will converge in extraordinary ways. Foundational AI tools like Claude Code, advances in agentic reasoning, open-source model innovations, and industry-specific deployments are shifting software engineering and scientific research into new paradigms. Robotics growth and AI-enabled automation promise to transform workplaces and daily life, while educational and workforce changes prepare talent for this new era. These waves of progress pose societal questions but also unparalleled opportunities for creativity, productivity, and discovery. The epoch of AI-powered agents and autonomous systems is clearly underway, reshaping technology and humanity’s future.
